近日,清华大学黄翊东团队崔开宇等以「Phonon lasing enhanced mass sensor with zeptogram resolution under ambient conditions」为题在Chip上发表研究论文,利用光声晶体微腔中声子激射后的机械模式线宽压缩,实现了65仄克精度的声子激光质量传感器。共同第一作者为潘非和崔开宇,通讯作者为崔开宇和黄翊东。Chip是全球唯一聚焦芯片类研究的综合性国际期刊,是入选了国家高起点新刊计划的「三类高质量论文」期刊之一。

质谱分析可用于确定样品的分子量、元素组成和结构信息,在生物、化学、医疗诊断、环境监测等领域都发挥着重要的作用。基于机械谐振子的质量传感器,可以通过探测粒子附着到振子后声学模式振动频率的变化来实现对粒子质量的传感(图1a)。这里声子的频率线宽相当于它的刻度,刻度越细锐,测量精度也越高(图1b)。但是在常温常压条件下机械损耗较大,难以实现超高灵敏度的质量传感,因此,仄克及更高分辨率的质量传感器通常需要在高真空或者超低温下实现¹⁻²。
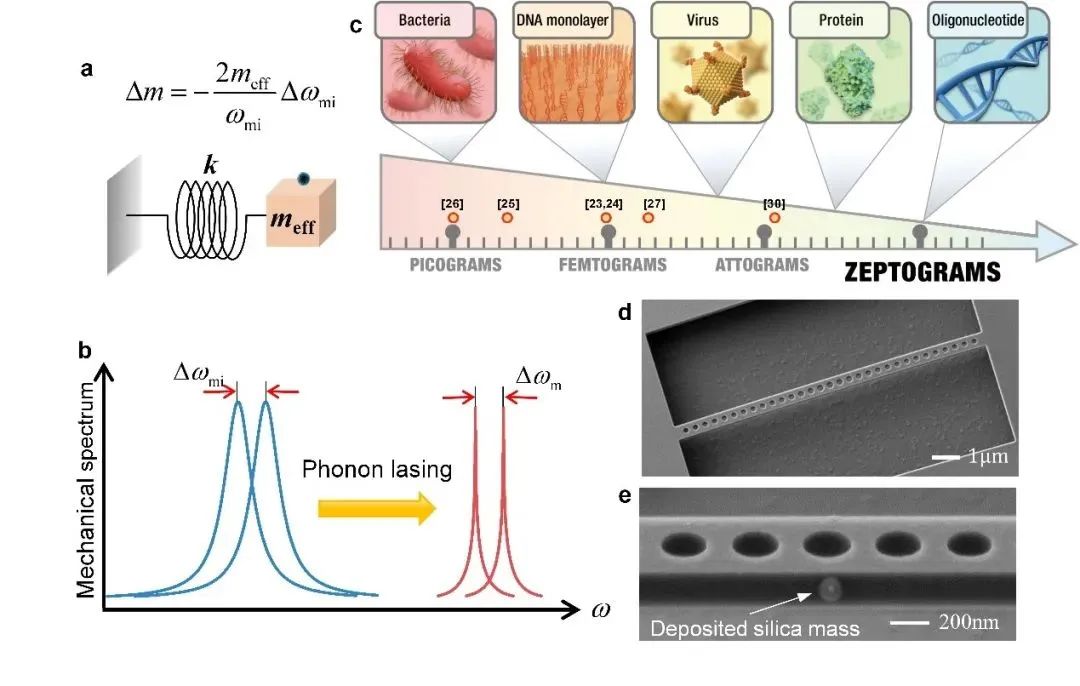
图1 | 基于机械谐振子的质量传感。a.质量传感原理图;b. 超窄线宽声子激射提高质量分辨率的原理;c.微观生物传感时的质量分辨率要求;d.光声晶体微腔的扫描电子显微镜图像;e.聚焦离子束沉积二氧化硅颗粒的扫描电子显微镜图像。
本研究工作提出在纳米悬臂梁光声晶体微腔中实现声子激射,利用激射后的超窄机械模式线宽³实现在常温常压环境下仄克量级的声子激光质量传感器。
纳米悬臂梁光声晶体微腔⁴⁻⁵的结构如图2a所示,两侧为周期性圆孔组成的反射区,中心为圆孔逐渐增大的缺陷区,在缺陷区中可以同时束缚光场和机械位移场。在光声晶体微腔中泵浦蓝失谐的激光,利用光场和机械场之间的耦合为声子模式提供增益,当声子激射后,声子模式线宽可以从2.6 MHz降低到5.4 kHz。
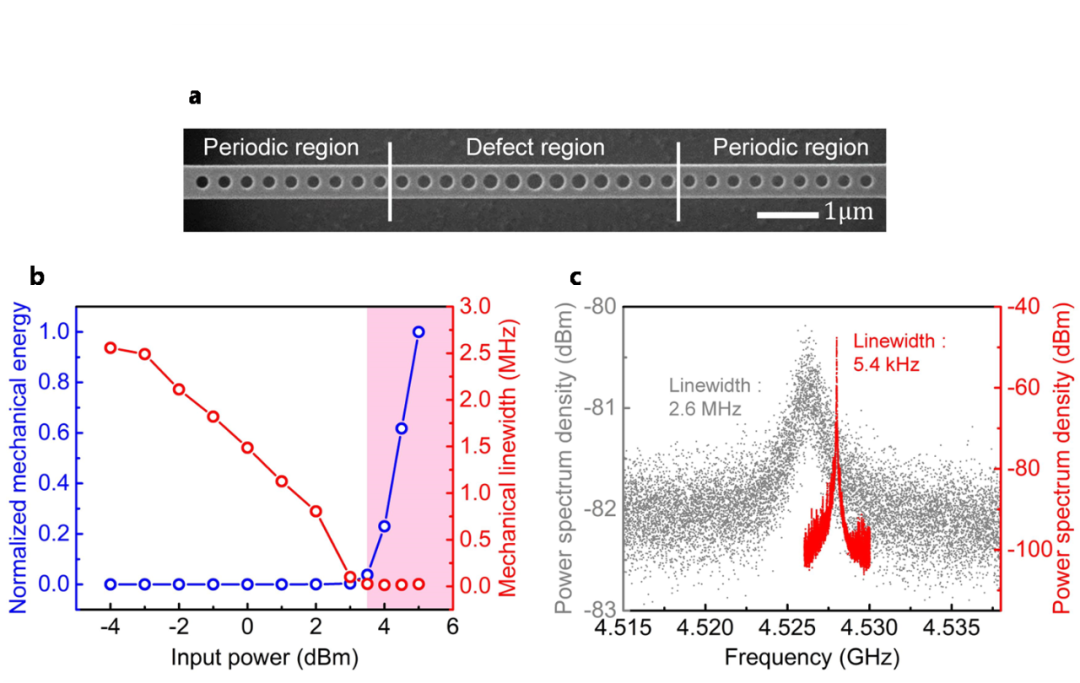
图2 | 纳米臂光声晶体微腔的声子激射。a.光声晶体微腔的扫描电子显微镜图;b.声子激射曲线;c.声子激射线宽;
实验中利用聚焦离子束沉积的方法在百纳米尺度下实现对微腔指定位置的沉积操作,用沉积的质量块来模拟微小的粒子进行微腔传感性能的验证;如图3所示,根据不同质量下的声子频率响应可以计算得到传感斜率 ,据此计算可测量的质量精度可达65仄克( )。这与已报道的利用微纳机械振子在常温常压环境中实现的最小可探测质量相比减小了约1个数量级以上,为下一代片上质量传感技术提供了一种可行的方案。
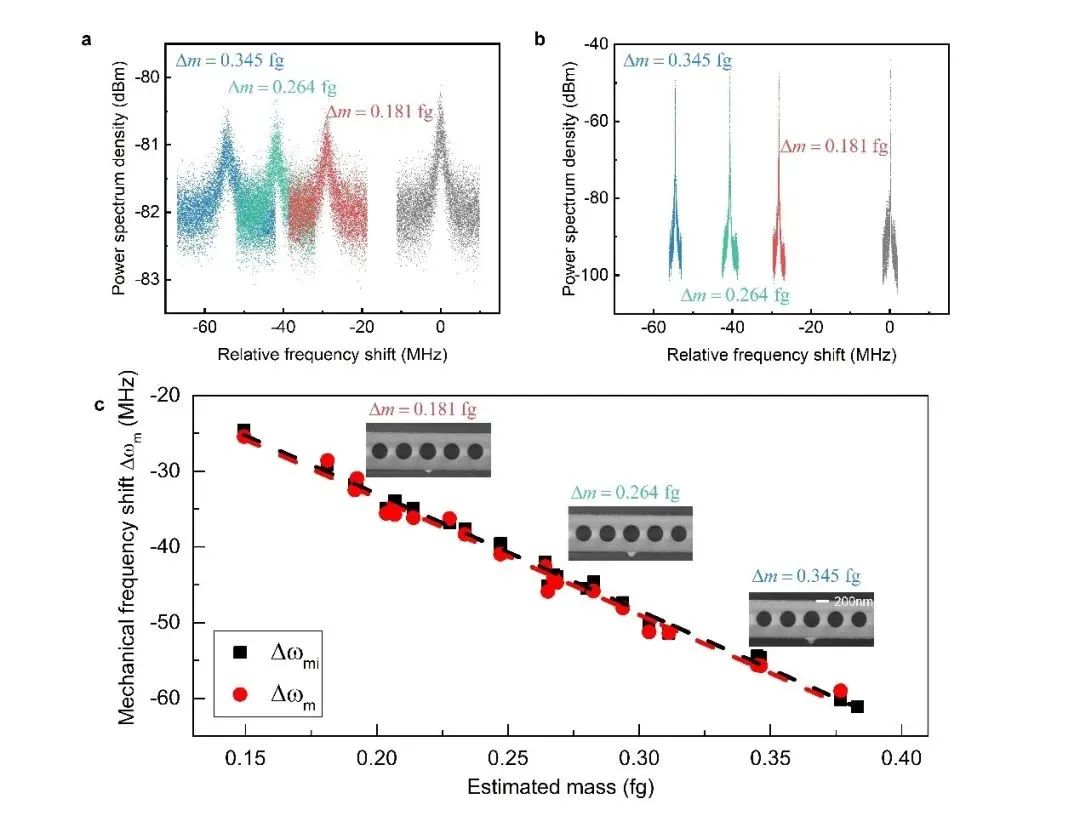
图3 | 质量传感实验。a.激射前声子峰随加载质量块的移动;b. 激射后声子峰随加载质量块的移动;c.声子峰变化对应的传感质量。
Phonon lasing enhanced mass sensor with zeptogram resolution under ambient conditions
Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique that is widely adopted to determine the molecular mass of samples, elemental composition and structural information, making it an indispensable tool in qualitative and quantitative applications including biological research, chemical measurements, astrophysical analysis and environmental monitoring. Based on the principle of mass sensing for mechanical oscillators, a higher intrinsic vibrational frequency, smaller effective mass, and smaller intrinsic mechanical frequency shift could lead to a higher mass resolution. Over the past decade, mass resolutions from zeptograms to yoctograms have been achieved by employing mechanical oscillator-based structures in a vacuum or cryogenic environment¹⁻². However, due to the large mechanical dissipation caused by the hydrodynamic force in the ambient environment, ultrasensitive mass sensing under ambient conditions has not yet been reported.
In our work, a new approach that utilizes phonon lasing to achieve an ultra-narrow mechanical linewidth³ was proposed, it allows a predicted maximum mass resolution of up to zeptograms at room temperature in an ambient environment. The designed sensor structure is an optomechanical crystal cavity⁴⁻⁵, as shown in Fig. 1d, which is referred to as the hole in the center defect region and exhibits a larger radius than that on both sides. In this system, the blue detuned pump light is scattered to lower frequency due to the mechanical motion, providing energy to the mechanical system. After phonon lasing, the mechanical linewidth is narrowed from 2.6 MHz to 5.4 kHz.
In the experiment, a small amount of silica was deposited by a focused ion beam (FIB) on the side wall of the optomechanical cavity, resulting in a mechanical frequency shift. The responsivities were measured in the signed optomechanical cavity, as shown in Fig. 3. Therefore, the minimum detectable mass is predicted to be . This high-resolution is an order of magnitude higher than those estimated using the reported routine approaches with Allan deviation and shows the potential application of the ultra-sensitive mass sensing in various fields such as biological research, gas sensing and environmental monitoring under ambient conditions.
参考文献:
1. Jensen, K., Kim, K. & Zettl, A. An atomic-resolution nanomechanical mass sensor. Nat. Nanotech. 3, 533–537 (2008).
2. Chaste, J. et al. A nanomechanical mass sensor with yoctogram resolution. Nat. Nanotech. 7, 301–304 (2012).
3. Xiong, J. et al. Phonon and photon lasing dynamics in optomechanical cavities. Fundam. Res. 3, 37–44 (2023).
4. Cui, K. et al. Phonon lasing in a hetero optomechanical crystal cavity. Photon. Res. 9, 937-943 (2021).
5. Wu, N. et al. On-chip mechanical exceptional points based on an optomechanical zipper cavity. Sci. Adv. 9, eabp8892 (2023).
论文链接:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2709472323000138
作者简介

潘非
2020年8月博士毕业于清华大学电子工程系,研究方向是光声晶体微腔、大气环境下的高精度传感。
Fei Pan
graduated from the Department of Electronic Engineering of Tsinghua University in August 2020. Her research work focused on photonic crystals and high resolution sensing under ambient conditions.

崔开宇
清华大学电子工程系长聘副教授、周炳琨学者,国家级青年人才。研究方向为基于光子/光声晶体、超表面的智能感知光电子器件,主持科技部重点研发计划、国家自然科学基金、北京市科技计划等项目。现为Photonics Insights 青年编委,Scientific Reports编委,北京与光科技、光函数有限公司创始人/首席科学家
Kaiyu Cui
is a Tenured Associate Professor and the Bingkun Zhou Scholar at the Department of Electronic Engineering of Tsinghua University. She has published more than 80 journal papers on nanophotonics, focusing on photonic crystals, metasurfaces, and optomechanical crystals. She is the founder of Seetrum and Lightfunction Corporation, Limited. She was awarded the National Distinguished Young Scholar of China. Moreover, she served as the Young Editor of Photonics Insights and an Editorial Board Member for Scientific Reports.

黄翊东
清华大学学术委员会副主任,长期从事光电子器件领域的科学研究及人才培养工作,曾任清华大学电子工程系系主任,清华大学天津电子信息研究院院长,是清华大学电子信息大类课程体系的主要创建人之一。发明“八分之一波长位移分布反馈”的新结构,开发出光通信抗反射DFB激光器,两次获得NEC研究功绩奖;近二十年来聚焦微纳结构光电子器件,承担过国家自然科学基金重点项目、973项目以及多项国际合作项目,带领课题组研制出世界首创具有自由电子辐射、实时光谱成像、动态轨道角动量辐射、量子态产生及操控等功能的集成光电子芯片;发表论文300余篇,引用数千次;申请专利182项(国际专利56项)。是光电子芯片企业华慧芯、与光科技、光函数科技的创始人。现为美国光学学会会士,中国光学学会常务理事,中国电子教育学会副理事长、高等教育分会副会长,ACS Photonics杂志副主编。
Yidong Huang
is the deputy director of the Academic Committee of Tsinghua University, Changjiang Distinguished Professor, and a national candidate of the New Century and Ten Million Talents Project. She has long been engaged in scientific research and talent cultivation in the field of optoelectronic devices. She was chair of the Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, and the first founding dean of the Institute for Electronics and Information Technology in Tianjin, Tsinghua University. She is one of the main founders of the electronic information curriculum system of Tsinghua University.
Professor Huang is presently engaged in research on nano-structure optoelectronics. She authored/co-authored more than 300 journal and conference papers and holds 182 patents. She is the founder of H-chip Tech Co., Ltd, Seetrum Tech Co., Ltd, and Lightfunction Tech Co., Ltd.Professor Huang is a Fellow of OSA, deputy member of Director Board of Chinese Optical Society, vice president of Chinese Electronic Education Association, and associate editor of ACS Photonics.
来源|FUTURE 远见 闵青云
审核|汪 玉 李冬梅